29 March 2021: Articles 
A 34-Year-Old Male Intravenous Drug User with a Third Episode of Tricuspid Valve Endocarditis Treated with Repeat Valve Surgery
Unusual clinical course
Jeffrey W. Cannon1BEF*, J.W. Awori Hayanga2AE, Thomas B. Drvar3BE, Matthew Ellison4E, Christopher Cook2AE, Muhammad Salman2AE, Harold Roberts2AE, Vinay Badhwar2E, Heather K. Hayanga4ADEDOI: 10.12659/AJCR.927385
Am J Case Rep 2021; 22:e927385
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Intravenous drug use is an epidemic in the United States. One of the complications of intravenous drug use can be infective endocarditis. The treatment for this disease is a combination of intravenous antibiotics, cardiac surgery consultation, and multidisciplinary psychiatric care. Despite surgical intervention, recurrence of disease is common. In the setting of recurrent infective endocarditis in the setting of intravenous drug use, the ethics of redo cardiac surgery has not been well-established.
CASE REPORT: A 34-year-old man with history of intravenous drug use presented on 3 separate occasions with infective endocarditis resulting in 3 tricuspid valve surgeries within fewer than 7 months. He said he had not injected drugs since before his first operation, he was considered to have a strong social support system, and he completed his postoperative antibiotic regimens each time. However, prior to his last operation, the patient had a urine drug screen positive for opiates without recorded prescribed opioids. Pathology reports from the 3 intraoperative specimens showed different pathogens each time. An extensive interprofessional discussion ensued.
CONCLUSIONS: Infective endocarditis in the setting of intravenous drug use and its treatments continue to be a point of ethical and medical discussion for all professionals involved with the care of these patients. This case could be used as an example of individualized decision-making, with rigorous ethical and medical discussion factoring into each decision for cardiac surgery. The ongoing treatment for patients with recurrent endocarditis in the setting of intravenous drug use requires more research and guidelines to help medical professionals better care for this patient population.
Keywords: Endocarditis, Ethics, Clinical, Substance Abuse, Intravenous, drug users, Endocarditis, Bacterial, Tricuspid Valve
Background
In 2017, more than 70 000 people died as a result of a drug overdose in the United States [1]. More than two-thirds of those deaths were related directly to opioids. With intravenous injection, the reuse of contaminated or shared needles leads to an increased risk of infective endocarditis. Infective endocarditis is a disease that has been increasing in incidence over the last 20 years [2]. Treatment typically involves intravenous antibiotics that are continued for 6 to 8 weeks [3,4]. Some patients require cardiac surgery with valve repair or replacement as definitive treatment [3]. However, the potential for reinfection of the new prosthetic valve exists; in this scenario, another cardiac surgery may be required, further increasing the risk of adverse outcomes [5]. The risk of mortality in patients with intravenous drug use (IVDU) having a redo valve surgery is double that of patients who only have 1 valve surgery [6]. If the recurrent infection is due to continued IVDU, the ethics of appropriate clinical management often comes to the fore-front [6, 7]. The ethics underlying the decision to operate is not well defined in the literature. While some research has focused on the short- and long-term outcomes of IVDU patients who underwent 1 or more cardiac valve surgeries, there is a relative dearth of guidelines on benefits and risks of repeated cardiac operations from both a biological and ethical perspective in this patient population [6–10].
We present a case in which a third tricuspid valve (TV) surgery was performed on a patient with a history of IVDU with partial recidivism. We seek to provide the course of action and decision-making at each juncture with the available clinical data. Our aim is to add to the clinical and ethical data in the literature to help guide future decisions and guidelines about how to treat infective endocarditis in an IVDU patient.
Case Report
A 34-year-old male presented to an outside hospital in September 2018 with complaints of weakness and lethargy. He had a right forearm abscess that was incised and drained. The culture of that abscess grew
Computed tomography (CT) angiography showed septic pulmonary emboli, and a CT brain was negative for abscess or emboli. A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) performed 4 days after presentation showed a 2-centimeter TV vegetation with severe TV regurgitation (Figure 1). Of note, the patient was hepatitis C reactive but ribonucleic acid polymerase chain reaction did not detect virus in the blood. The patient was transferred to our hospital for cardiac surgery consultation. Nine days after initial presentation, the patient had autologous TV repair, partial papillary muscle excision, and patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure. The intraoperative specimen of the TV grew
In January 2019, the patient returned to the clinic for repeat TEE to evaluate for postoperative TV regurgitation, and it showed an annuloplasty ring in the tricuspid position with evidence of severe tricuspid regurgitation. He was admitted to the hospital from the clinic due to worsening shortness of breath, bilateral lower-extremity edema, fatigue, fever, and chills. The patient reported having only felt better clinically for a few weeks after the initial cardiac surgery. He and his mother said he had no recurrent use of intravenous drugs but had stopped taking buprenorphine and naloxone. He was a current tobacco smoker, but he abstained due to his respiratory symptoms. Six days after presentation, a TV replacement with a 29-mm St. Jude Medical Epic heart valve (St. Jude Medical Inc., St. Paul, Minn., USA) and a repeat PFO closure were performed. At the time of surgery, blood cultures were negative but a vegetation was visualized on the repaired TV with severe regurgitation (Figure 2). An intraoperative specimen of the TV grew mitis group viridans streptococcus. The patient received 6 weeks of intravenous antibiotics, and he was discharged home in early March 2019. His length of stay was 47 days. As an outpatient, he had medical and psychiatric follow-up.
In March 2019, the patient presented to our hospital from an outside hospital after falling off a ladder 4 days prior. His shoulder had been reduced at the outside hospital on the day of the fall, and he had been discharged. However, he went home and developed symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, and chills. He returned to the outside hospital, where he had blood cultures that grew
Discussion
The incidence of infective endocarditis has been increasing over the last 20 years [2]. Specifically for TV infective endocarditis, approximately 5–16% of patients will require cardiac surgery, even with successful antibiotic treatment [8]. The likelihood of an infected prosthetic valve requiring surgery is higher; thus, valve repair is favored over replacement when feasible [8]. First-time isolated TV infective endocarditis patients have operative mortality rates of 0–15% [8]. The 2- and 5-year survival rates following cardiac surgery for IVDU infective endocarditis are 79% and 59%, respectively [9]. With regard to morbidity, IVDU patients with TV infective endocarditis who undergo cardiac surgery are at risk for reinfection [8]. In the short-term (3 to 6 month) postoperative period, IVDU patients are at a 10-times higher risk of reoperation or death compared to postoperative non-IVDU patients [5,6].
Another consideration regarding infective endocarditis patients with IVDU is that they may concomitantly have other infectious complications that further complicate the clinical picture. These patients may also have human immunodeficiency virus or other transmissible infections such as hepatitis C, necessitating special precautions and safeguards to reduce the potential for viral transmission during surgery. Several other teams may be involved with the care of these patients as well. For example, patients may also have mycotic femoral and brachial pseudoaneurysms that need to be addressed by a vascular surgery team [14]. Thoracic surgery may also be involved. Medical subspecialities may include neurology for guidance regarding septic brain emboli, infectious diseases for antibiotic management, cardiology for echocardiographic evaluation, and psychiatry, among others. These co-morbidities must also be considered in a benefit-risk discussion and an ethical analysis. The goal of these ethical considerations should be to find a balance in the competing concerns, namely the care of the patient and the safety of those caring for the patient.
The discussion of high-risk cardiac surgery in recurrent prosthetic valve infection in IVDUs has led to ethical and economic considerations [12]. This discussion stage is where many institutions reside today regarding the approach to redo valve replacement [12,13]. Numerous clinical guidelines and systematic reviews regarding infective endocarditis in the setting of IVDU address the medical and surgical needs of these patients [9,10,18–20]. However, the ethics behind these decisions are often not addressed. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) guidelines mention that IVDU infective endocarditis patients should be offered cardiac surgery, but they do not clearly delineate how to decide on repeat cardiac operations [14]. The 2015 European Society of Cardiologists guidelines for management of infective endocarditis do not offer explicit guidance on how to approach the ethics of repeat operations in IVDU patients [15]. Similarly, the American Heart Association, in their 2015 statement on infective endocarditis, does not make mention of the ethics of redo valve procedures in the setting of IVDU [3]. There is a need for clear ethics guidelines to help guide treatment for IVDU infective endocarditis patients, especially those with reinfection of a valve.
The ethics of redo cardiac surgery in patients with IVDU who have infective endocarditis illustrates the bioethical principle of justice (Table 2). Justice is defined as the judicious appropriation and use of the medical resources in a society [16,17]. Cardiac surgery and its associated resource allocation may be considered a scarce resource. Thus, the ethics of a redo valve replacement or repair in this patient population are subject to ongoing debate. The decision of how to proceed with IVDU infective endocarditis patients’ care should be multidisciplinary, including all teams who will care for the patient. One method that shows promise in improving outcomes is the involvement of the inpatient psychiatry and addiction team(s) in caring for an IVDU infective endocarditis patient. These teams can provide in-hospital opioid agonist treatment and start the process of identifying outpatient treatment availability once the patient is discharged [21,22]. A study by Suzuki et al showed almost two-thirds of IVDU infective endocarditis patients engaged with buprenorphine treatment in hospital or accepted referral to a methadone maintenance following discharge [22]. A study by Yeo et al argues that a recidivist IVDU infective endocarditis patient who is not compliant with abstinence from substance use should not be offered a second valve [7]. However, others are changing their practice to offer redo cardiac surgeries and implementing ethical analysis to guide the decision-making [18, 19]. Discussions have been ongoing among surgeons regarding their moral, ethical, and medical obligations to perform a second valve replacement or beyond, with cases being made for both sides of the issue [20,21,23,24].
Conclusions
We presented a case of a patient with history of IVDU who underwent triple redo TV surgery, with different organisms causing infective endocarditis each time. Applying the aforementioned principles, the best chance at improving outcomes and prolonging survival is early involvement with psychiatry for treatment of the addiction prior to and after the valve replacement, with both inpatient and outpatient treatment being recommended. This interdisciplinary approach ensures each patient receives optimal care.
Figures
References:
1.. Scholl L, Seth P, Kariisa M, Drug and opioid-involved overdose deaths – United States, 2013–2017: MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2019; 67; 1419-27
2.. Cresti A, Chiavarelli M, Scalese M, Epidemiological and mortality trends in infective endocarditis, a 17-year population-based prospective study: Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2017; 7(1); 27-35
3.. Baddour LM, Wilson W, Bayer A, Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association: Circulation, 2015; 132; 1435-86
4.. Yung D, Kottachchi D, Neupane B, Antimicrobials for right-sided endocarditis in intravenous drug users: A systematic review: J Antimicrob Chemother, 2007; 60; 921-28
5.. Shrestha NK, Jue J, Hussain S, Injection drug use and outcomes after surgical intervention for infective endocarditis: Ann Thorac Surg, 2015; 100(3); 875-82
6.. Mori M, Mahmoud S, Schranz A, Risk of reoperative valve surgery for endocarditis associated with drug use: J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2020; 159(4); 1262-68
7.. Yeo KK, Chang WJ, Lau JM, Tan SY, Valve replacement in endocarditis: Setting limits in noncompliant intravenous drug abusers: Hawaii Med J, 2006; 65(6); 168-71
8.. Pfannmueller B, Kahmann M, Davierwala P, Tricuspid valve surgery in patients with isolated tricuspid valve endocarditis: Analysis of peri-operative parameters and long-term outcomes: Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2017; 65(8); 626-33
9.. Aultman JM, Peshel E, Harfouche C, Firstenberg MS, The ethics in repeat heart valve replacement surgery, advanced concepts in endocarditis, 2018
10.. Ahmed T, Safdar A, Ethical dilemma: Should continuous intravenous drug use affect appropriate management in prosthetic valve endocarditis?: Cureus, 2020; 12(6); e8458
11.. Hussain ST, Witten J, Shrestha NK, Tricuspid valve endocarditis: Ann Cardiothorac Surg, 2017; 6(3); 255-61
12.. Østerdal OB, Salminen PR, Jordal S, Cardiac surgery for infective endocarditis in patients with intravenous drug use: Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2016; 22(5); 633-40
13.. Kim JB, Ejiofor JI, Yammine M, Surgical outcomes of infective endocarditis among intravenous drug users: J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2016; 152(3); 832-41
14.. Domanin M, Romagnoni G, Romagnoli S, Emergency hybrid approach to ruptured femoral pseudoaneurysm in HIV-positive intravenous drug abusers: Ann Vasc Surg, 2017; 40; 297.e5-12
15.. Gansera LS, Eszlari E, Deutsch O, High-risk cardiac surgery in patients with intravenous drug abuse and/or active hepatitis C or HIV infection: An ethical discussion of six cases: Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2016; 64(1); 2-5
16.. Beauchamp TL, Childress JF: Principles of biomedical ethics, 2001, New York, Oxford University Press
17.. Gillon R, Lloyd A: Principles of health care ethics, 1994, Chichester, Wiley
18.. Sanaiha Y, Lyons R, Benharash P, Infective endocarditis in intravenous drug users: Trends Cardiovasc Med, 2020; 30(8); 491-97
19.. Pettersson GB, Coselli JS, Hussain ST, 2016 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) consensus guidelines: Surgical treatment of infective endocarditis: Executive summary: J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2017; 153(6); 1241-58
20.. Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, 2015 ESC guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: Eur Heart J, 2015; 36; 3075-123
21.. Elbatarny M, Bahji A, Bisleri G, Hamilton A, Management of endocarditis among persons who inject drugs: A narrative review of surgical and psychiatric approaches and controversies: Gen Hosp Psychiatry, 2019; 57; 44-49
22.. Suzuki J, Medication-assisted treatment for hospitalized patients with intravenous-drug-use related infective endocarditis: Am J Addict, 2016; 25(3); 191-94
23.. Miljeteig I, Skrede S, Langørgen J, Should patients who use illicit drugs be offered a second heart-valve replacement?: Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen, 2013; 133(9); 977-80
24.. DiMaio JM, Salerno TA, Bernstein R, Ethical obligation of surgeons to noncompliant patients: can a surgeon refuse to operate on an intravenous drug-abusing patient with recurrent aortic valve prosthesis infection?: Ann Thorac Surg, 2009; 88(1); 1-8
Errate
Figures
Tables
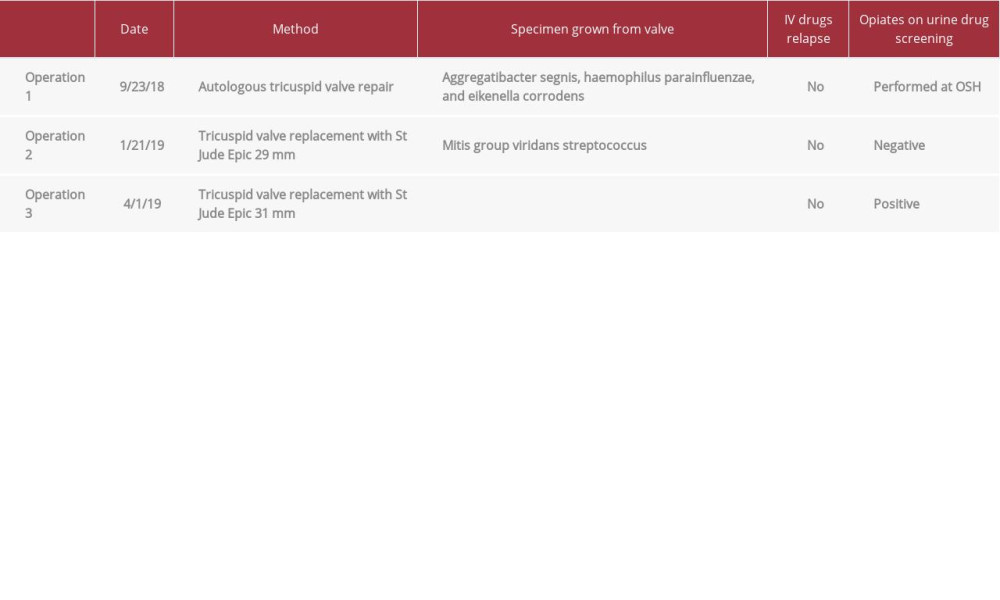 Table 1.. Timeline of surgical operations, pathology findings, reported intravenous drug use, and urine toxicology findings.
Table 1.. Timeline of surgical operations, pathology findings, reported intravenous drug use, and urine toxicology findings.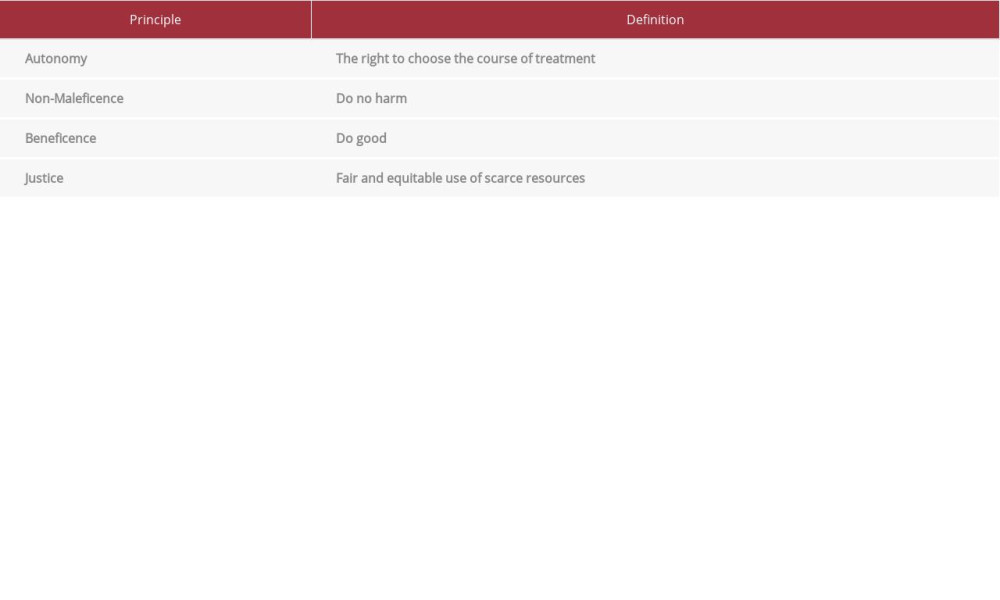 Table 2.. Bioethical principles and definitions [16,17].
Table 2.. Bioethical principles and definitions [16,17]. Table 1.. Timeline of surgical operations, pathology findings, reported intravenous drug use, and urine toxicology findings.
Table 1.. Timeline of surgical operations, pathology findings, reported intravenous drug use, and urine toxicology findings. Table 2.. Bioethical principles and definitions [16,17].
Table 2.. Bioethical principles and definitions [16,17]. In Press
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943420
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942824
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943118
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942826
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250








