14 August 2020: Articles 
Short-Term Corticosteroid Therapy for Early Exacerbation of COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report
Management of emergency care
Akira Urano1ABCDEF, Hajime Kasai123BDE*, Yushi Murai1BC, Hideki Ikeda1BC, Takashi Urushibara14ABCDEFDOI: 10.12659/AJCR.924476
Am J Case Rep 2020; 21:e924476
Abstract
BACKGROUND: The effect of corticosteroids in the management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is unclear.
CASE REPORT: A 67-year-old man who tested positive for COVID-19 by reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) analysis was admitted to our hospital. On admission, he had no dyspnea and his oxygen saturation (SpO₂) level was normal. Chest imaging revealed ground-glass opacities (GGO) distributed in both lung fields. Four days after admission, bilateral lung shadows worsened, with a slight reduction in SpO₂ levels. Short-term corticosteroid therapy was initiated, and SpO₂ and radiographic findings promptly improved without use of antiviral agents.
CONCLUSIONS: More data are required to ascertain the role of corticosteroids in the management of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Keywords: Coronavirus Infections, Pneumonia, Viral, SARS Virus, Glucocorticoids, COVID-19, Betacoronavirus, COVID-19, Drug Administration Schedule, Lung, Methylprednisolone, Oxygen, Pandemics, SARS-CoV-2, Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and was first reported at the end of 2019; it is now spreading worldwide [1]. On March 11, 2020, the WHO characterized COVID-19 as a pandemic [2]. A Chinese study reported that the mortality rate of COVID-19 is 2.3% in China, which is not as high as that of SARS or Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS); however, the elderly and patients with underlying comorbidities are at a higher risk of the disease and its related mortality [3]. Although several antimicrobial agents, including arbidol [4], oseltamivir, ganciclovir [5], lopinavir/ritonavir [6,7], chloroquine [8], and remdesivir [9], have been assessed for COVID-19 treatment, no effective treatment has been established thus far. Furthermore, corticosteroid treatment is not currently recommended for COVID-19 patients [10]. Here, we present the case of a patient with COVID-19 whose condition improved with short-term systemic corticosteroid treatment early after exacerbation of pneumonia.
Case Report
A 67-year-old man who had traveled on a cruise ship was hospitalized because of fever and headache 6 days before admission. Reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR)-based screening for SARS-CoV-2 from a throat swab performed on the ship revealed a positive result. In accordance with national standards at the time, hospitalization was required for all positive patients. Therefore, the patient was hospitalized and monitored, without oxygen therapy. His symptoms included only fever and headache. The patient had no remarkable medical history or comorbidities except for cholecystitis. He was not receiving any long-term medication.
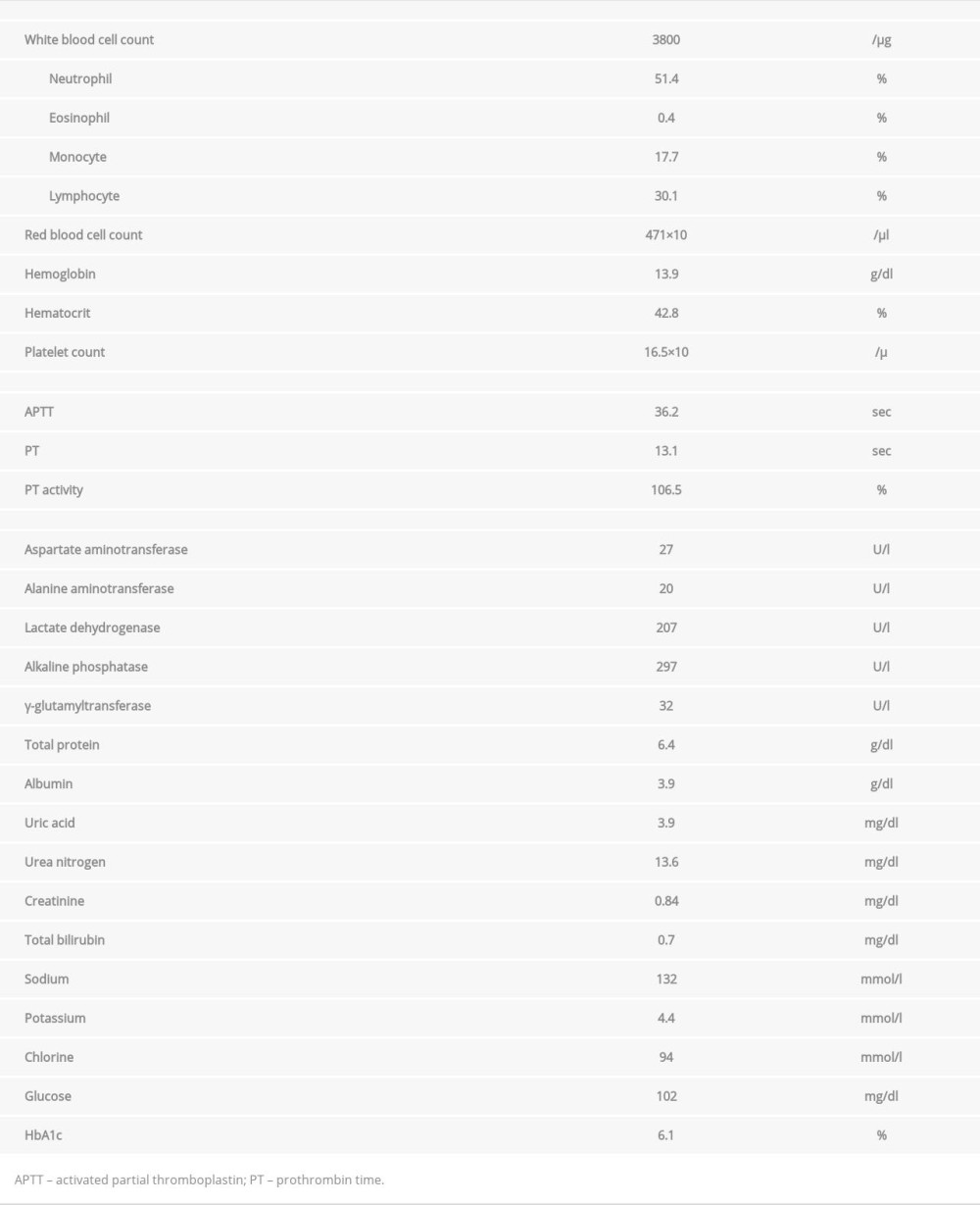
On admission, the patient’s vital signs included a body temperature of 37.4°C; blood pressure, 134/77 mmHg; pulse, 78/min; respiratory rate, 16/min; and oxygen saturation (SpO2), 96% on ambient air. Physical examinations revealed no abnormalities. Laboratory investigations revealed elevated C-reactive protein (CRP, 2.89 mg/L) and white blood cell count of 3.8×109/L (neutrophils, 51.4%; lymphocytes, 30.1%) (Table 1). Chest X-rays revealed diffuse infiltrates (Figure 1) and computed tomography (CT) imaging revealed bilateral ground-glass opacity (GGO) in subpleural areas (Figure 2). Based on imaging findings and RT-PCR testing, the patient was diagnosed with COVID-19 pneumonia. Initially, the patient’s respiratory condition was stable, and he was examined almost daily by chest X-ray imaging, without medication and oxygen therapy. On hospitalization day 5, chest X-rays revealed worsening of diffuse infiltrates (Figure 1) and laboratory investigations revealed CRP levels of 4.09 mg/L and a white blood cell count of 4.6×109/L (neutrophils, 52.5%; lymphocytes, 27.2%), with a reduction in SpO2 to 92% on ambient air. Short-term corticosteroid therapy (i.v. administration of 125 mg methylprednisolone every 12 hours) was administered on hospitalization days 5, 6, and 7; consequently, SpO2 and radiographic findings improved from hospitalization day 6 (Figure 1). The symptoms did not exacerbate after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment. However, despite improvement in SpO2, the patient could not be discharged owing to the positive result of an RT-PCR test performed on hospitalization day 14. Finally, RT-PCR tests of nasopharyngeal swabs and throat swabs yielded negative results on hospitalization days 16 and 17. The patient was then discharged on hospitalization day 18.
Discussion
This study reports the case of a COVID-19 patient with improved overall conditions after short-term systemic corticosteroid treatment early after the exacerbation of pneumonia. Our findings suggest that systemic corticosteroid therapy may be a potential treatment alternative for exacerbated COVID-19 pneumonia. Moreover, the present case potentially provides novel insights into the application of corticosteroids for treating COVID-19.
In some respiratory infections, a mortality benefit has been achieved through timely administration of corticosteroids [11,12]. A meta-analysis by Siemieniuk et al. reported that systemic corticosteroid therapy can reduce mortality in community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization [13]. Moreover, corticosteroids co-administered with anti-Pneumocystis therapy can decrease the mortality rate and respiratory failure associated with Pneumocystis pneumonia among patients with human immunodeficiency virus infections [12]. However, the benefits of corticosteroid treatment in influenza remain unknown [14]. Corticosteroids were often prescribed empirically to SARS and MERS patients [15,16]. However, corticosteroid administration for COVID-19 patients is not recommended thus far; this includes patients with severe pulmonary injury or shock, based on evidence from other viral infectious diseases, including SARS or MERS [10]. In the present case, SpO2 and radiographic findings improved the day after systemic corticosteroid treatment was initiated, with no exacerbation of respiratory status or pneumonia, after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment. Administration of lopinavir/ritonavir was considered if pneumonia had not improved the day after the initiation of corticosteroid therapy. However, the patient’s condition improved without additional treatment, suggesting that some COVID-19 patients can benefit from systemic corticosteroid therapy.
However, it remains unclear which COVID-19 patients benefit from corticosteroid treatment. Sung et al. reported that the administration of corticosteroids to patients with SARS, relatively early after onset, yielded a favorable outcome [15]. Previous studies have reported that in acute viral respiratory infections, early-response cytokines, including interferon-tumor necrosis α, interleukin (IL)-1, and IL-6, are produced at high levels and mediate antiviral activity; however, they simultaneously potentially contribute to tissue injury [17,18]. Early corticosteroid therapy among SARS patients may have prevented death by regulating cytokine responses [15]. Similarly, in the present case, early corticosteroid treatment may have suppressed such an inflammatory burst in a COVID-19 patient, thus preventing the need for ventilator management. However, corticosteroid treatment was reportedly ineffective among MERS patients in an intensive care unit; the general condition of the patients was not serious enough to warrant admission to the intensive care unit, whereas previously reported subjects had a severe pathological condition [16]. The present case report included only 1 patient and the patient’s condition might have improved spontaneously without corticosteroid treatment. Although the exact role of corticosteroid treatment cannot be determined owing to limited data, corticosteroid treatment in the early stage of COVID-19 pneumonia exacerbation may be considered a potential treatment alternative.
Conclusions
Our findings indicate that corticosteroid treatment can benefit cases of mild and early-stage exacerbation of pneumonia among COVID-19 patients; however, this was an uncontrolled observation and warrants further controlled clinical trials. Additional cases need to be studied to determine the precise symptoms of COVID-19 patients who would benefit most from systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Figures
References:
1.. , Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report – 1. 21 January 2020 Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/
2.. , Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation report – 51. 11 March 2020 Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/
3.. , [The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) in China]: Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2020; 41(2); 145-51 [in Chinese]
4.. Zhang J, Zhou L, Yang Y, Therapeutic and triage strategies for 2019 novel coronavirus disease in fever clinics: Lancet Respir Med, 2020; 8(3); e11-12
5.. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study: Lancet Respir Med, 2020; 8(5); 475-81
6.. Lim J, Jeon S, Shin HY, The Author’s Response: Case of the index patient who caused tertiary transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea: The application of lopinavir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia monitored by Quantitative RT-PCR. J Korean Med: Sci, 2020; 35(7); e89
7.. Kim JY, Letter to the Editor: Case of the index patient who caused tertiary transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 in Korea: The application of lopinavir/ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia monitored by Quantitative RT-PCR. J Korean Med: Sci, 2020; 35(7); e88
8.. Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X, Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies: Biosci Trends, 2020; 14(1); 72-73
9.. Lai CC, Shih TP, Ko WC, Severe acute respiratory syndrome corona-virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges: Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2020; 55(3); 105924
10.. Russell CD, Millar JE, Baillie JK, Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury: Lancet, 2020; 395(10223); 473-75
11.. Stern A, Skalsky K, Avni T, Corticosteroids for pneumonia: Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017; 12(12); CD007720
12.. Ewald H, Raatz H, Boscacci R: Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015; 2015(4); CD006150
13.. Siemieniuk RA, Maeda MO, Alonso-Coello P, Corticosteroid therapy for patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia: A systematic review and meta-analysis: Ann Intern Med, 2015; 163(7); 519-28
14.. Lansbury L, Rodrigo C, Leonardi-Bee J, Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of influenza: Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019; 2(2); CD010406
15.. Sung JJ, Wu A, Joynt GM, Severe acute respiratory syndrome: Report of treatment and outcome after a major outbreak: Thorax, 2004; 59(5); 414-20
16.. Arabi YM, Mandourah Y, Al-Hameed F, Corticosteroid therapy for critically ill patients with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome: Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2018; 197(6); 757-67
17.. Cheung CY, Poon LL, Lau AS, Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: A mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease?: Lancet, 2002; 360(9348); 1831-37
18.. Van Reeth K, Van Gucht S, Pensaert M: Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 2002; 87(3–4); 161-68
Figures
In Press
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943687
17 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943070
17 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943370
18 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943803
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250